good-to-know
1969 – A year for the aviation history books
The year 1969 marked the history of aerospace like virtually no other with the moon landing, the foundations of world-class aviation groups, the start of the jumbo jet age and supersonic passenger travel.
author: Denis Dilba | 9 mins reading time published on: 01.03.2019
author:
Denis Dilba
holds a degree in mechatronics, is a graduate of the German School of Journalism, and founded the “Substanz” digital science magazine. He writes articles about a wide variety of technical and business themes.

A selection of the key events in aviation history from 1969
February
The ancestor of the jumbo jet, Boeing’s “RA001” 747 prototype, takes off from the U.S. company’s airport in Everett near Seattle. With a wingspan of 60 meters and distinctive cockpit hump, this 70-meter giant is still powered exclusively by Pratt & Whitney JT9D engines. From 1973 onwards, the jumbo would be equipped with the popular CF6-50 engine. Today, the CF6 series—for which MTU has been a risk and revenue sharing partner since 1971—remains one of the world’s most successful engine families.
March
Concorde takes off from Toulouse-Blagnac on its first test flight. Over the next few months, the supersonic passenger aircraft developed by the French and British aviation industries together would fly below the speed of sound; only in October would it first break the sound barrier. Concorde entered commercial service in 1976. However, supersonic passenger flight did not turn out to be big business, so much so that the two operating airlines Air France and British Airways retired the Concorde in late October 2003 after one of the jets crashed. Thanks to its slimline design and a top speed of up to 2,400 km/h, this aircraft still reigns as the queen of the skies.
May
At the Paris Air Show in Le Bourget, French transport minister Jean Chamant and German economic minister Karl Schiller sign the contract to build what would become the Airbus A300. A year after the contract signing, the Airbus Industrie consortium was founded. This marked the beginning of the end for the United States’ uncontested supremacy in the passenger aircraft market.
June
Following its maiden flight on New Year’s Eve 1968, the Tupolew Tu-144 becomes the first commercial supersonic aircraft to break the sound barrier in June 1969. However, the technically underdeveloped jet would enjoy just as little success as its West-European counterpart: the Tu-144 transported just 3,284 passengers on 55 flights. The development program was halted in 1983. Of the 16 aircraft produced, today only 5 are available to the public, including at the Technik Museum Sinsheim in Germany.
February

Jumbo jet: Until 2005, the Boeing 747 was the world’s largest passenger aircraft.
March
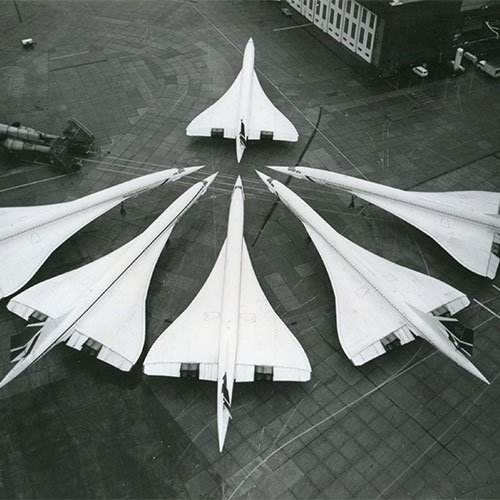

Queen of the skies: Despite its speed and sleek shape, the Concorde did not manage to make supersonic passenger flights into a sustainable business.
June
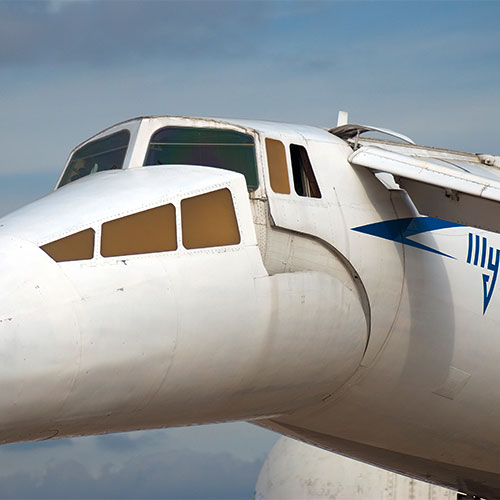

Droop nose: Both the Concorde and the Tupolev Tu-144 featured a nose cone that pilots could lower to improve visibility on the ground.
July

Groundbreaking: Founded 50 years ago, MTU München became MTU Aero Engines in the year 2000.
October
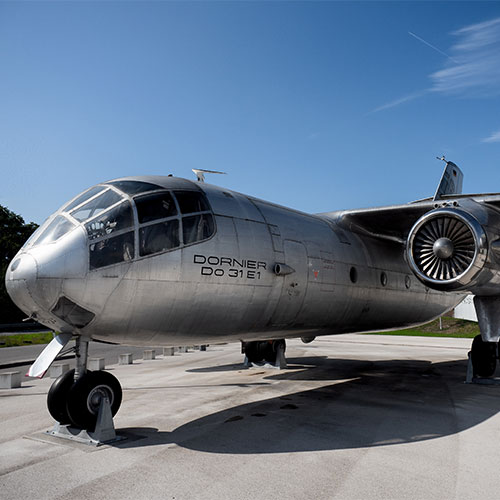

Vertical takeoff aircraft: To this date, the Do 31 remains the world’s only transport aircraft to achieve vertical takeoff and landing. In the picture: the prototype outside the Dornier museum in Friedrichshafen.
December
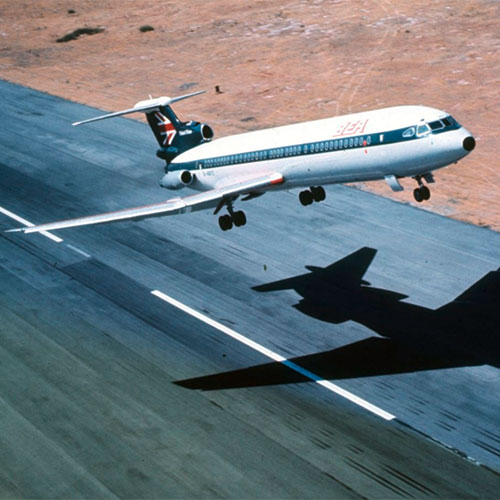

Short but sweet: The Trident 3B flew for only 17 years. Competition from Boeing with its quieter and more efficient aircraft was simply too tough.
July
On July 11, MTU Motoren- und Turbinen-Union München GmbH MAN Maybach Mercedes-Benz was founded, known as MTU München for short. Basis for the foundation is a contract between MAN Turbo GmbH and Daimler-Benz that defined the consolidation of the two companies’ turbo aircraft engine and high-speed diesel engine activities; in addition to MTU München (aircraft engines), MTU Friedrichshafen (diesel engines) was also founded.
On July 21 at 3:56 a.m. CET, U.S. astronaut Neil Armstrong became the first man on the moon. He was followed by Buzz Aldrin. Some 600 million TV viewers experience the event via live broadcast. Michael Collins, the third astronaut on the Apollo 11 mission, stayed on board the Columbia mothership, which could not orbit the moon independently. On July 24, Apollo 11 returned to Earth.
August
The Brazilian government founds Empresa Brasileira de Aeronáutica, better known as Embraer. After its privatization in 1994, the aviation group rises to become the fourth largest aircraft manufacturer behind Airbus, Boeing and Bombardier Aerospace.
September
Made by J. Wagner Helicoptertechnik, Friedrichshafen-Fischbach, the FJ-Sky-Trac is the first helicopter developed in Germany since the Second World War and receives type approval from the German Federal Aviation Office.
October
The German government ends the development program for the Dornier Do 31 vertical takeoff aircraft: due to a new NATO doctrine and a shift in German Armed Forces requirements, the concept is declared to have no future for military applications. The Do 31 is nevertheless a technical masterpiece and marks a milestone in aviation history. Today it remains the only jet-powered transport aircraft to achieve vertical takeoff and landing.
December
Trident 3B, made by British manufacturer Hawker Siddeley, takes off for the first time. Originally a three-engine aircraft, this Trident model was equipped with a fourth engine on its tail assembly to provide extra thrust during takeoff. This exotic aircraft was developed specially for British European Airways (BEA) and offered space for 180 passengers. Louder and consuming more kerosene than its rival, the Boeing 737, the 3B was retired by BEA in 1986.